|
|
| 18. HRV SDNN |
SDNN is a calculated parameter of Heart Rate Variability (HRV) that represents the standard deviation of normal-to-normal R-R-intervals. SDNN is expressed in milliseconds, and a normal value for this is over 50. However, SDNN values are also dependent on age and gender and normally become lower with age.
An individual's heartbeats do not occur at constant intervals, but rather with a small variance between them. HRV measures the variation in time between the heartbeats.
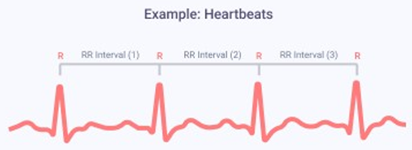
High levels of HRV generally indicate aerobic and general fitness. Athletes may track HRV to adjust their training program. They can learn when the body is being overworked, which often results in a drop in HRV, and can learn how fast they recover. Moreover, persons with high HRV may be more resilient to stress.
HRV measurements provide feedback about your lifestyle and can help inspire taking steps toward a healthier life. If you are implementing changes in your lifestyle such as meditation, better sleep, better nutrition, and participation in sports and physical activity, you may notice changes in the HRV. In addition, this could help to track your nervous system's reactions to the environment, emotions, thoughts, and feelings.
The sympathetic system (Stress Response) is activated when the body is under stress, causing the heart to beat faster and more regularly, and causing HRV to decrease. The parasympathetic system (Recovery Ability) manages the heart’s activity to help the body reach a relaxed state and to recover from a stressful event. This relaxation response results in a slower and less regular heartbeat and is indicated by a higher HRV.
If you have questions about your results, seek a doctor’s advice and they will let you know what’s normal for your specific condition. |
| |
|